These two modifies the conductance of the ions across the membranes of the cells of the SA node causing either an increase or a decrease in heart rate. Acetylcholine plays an important role in the ingestion of food and in the functioning of the digestive system.

Cardiac Physiology Anatomy And Physiology Ii
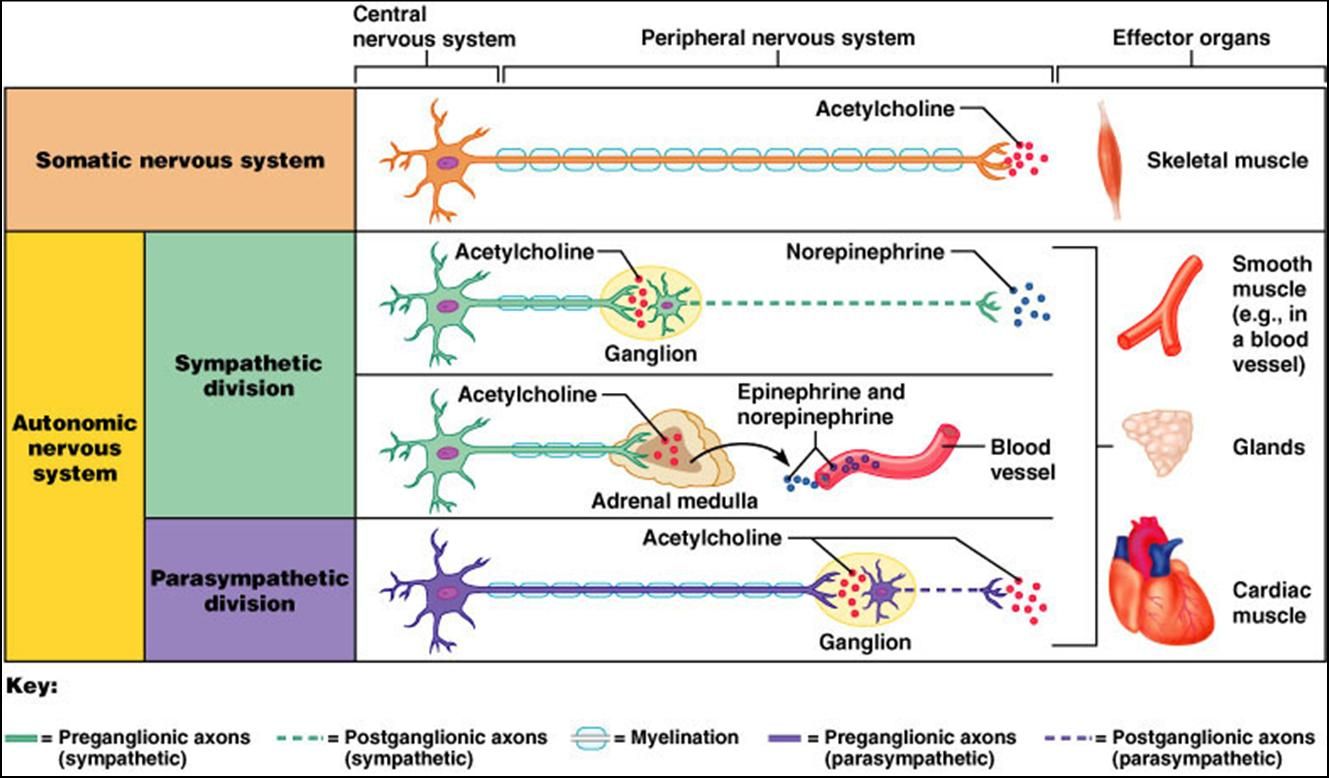
The sympathetic nervous system SNS releases the hormones catecholamines - epinephrine and norepinephrine to accelerate the heart rate.
. These transmitters act upon several different effector systems including several different kinds of ion channels in the. How does Acetylcholine decrease heart rate. Effects of acetylcholine on the heart.
Acetylcholine has an inhibitory effect on cardiac muscle it decreases heart rate. Epinephrine mimics the effects of which branch of the autonomic nervous system. The effect of acetylcholine on cardiac muscle however is very different from its effects on skeletal or smooth muscle.
This has the effect of slowing contraction of the heart muscle and making it beat with less force. Be able to explain the answers to the clinical applications questions and the normal physiology of the heart is affected. Effects of acetylcholine on the heart.
Impulses carried to the heart by means of fibers that secrete acetylcholine are what. Acetylcholine in the concentration used had no effect on any of the measured variables but did antagonize the effects of the three agonists on contractility and phosphorylase activity. It is not however obtained so regularly as on the mammalianheart.
The BP showed an initial gradual fall followed by a secondary precipitous fall. 10000 is applied to the frogs heart attached to a cardiograph in the usual way slowing and weakening is seen. How does ACh inhibit cardiac.
Together they cause the muscle to contract. An increase in heart rate requires an inhibition of vagus nerve stimulation or acetylcholine activity. The sympathetic nervous system SNS and the parasympathetic nervous system PNS.
Effects of acetylcholine on the heart Am J Physiol. Include receptors channels ion flowin describing the mechanisms Answer 8. Authors M R.
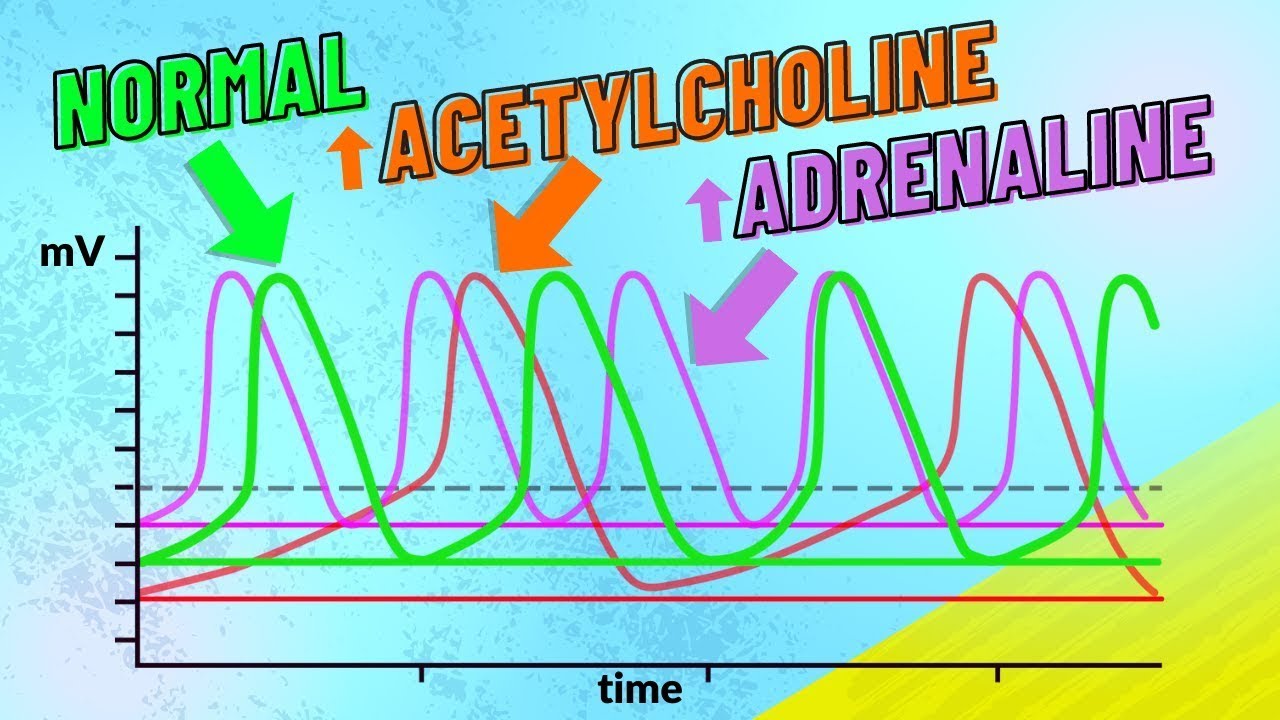
Watch and learn how it all works. Up to 10 cash back Abstract. 046 How Adrenaline and Acetylcholine Affect Heart Rate.
In humans and many other animals heart rate is slowed by the parasympathetic nervous system neurotransmitter. What effect does acetylcholine have on the heart rate. These channels initially called K Ach slow the depolarization of the pacemaker cell and decrease the heart rate.
The parasympathetic nervous system PNS releases the hormone acetylcholine to slow the heart rate. This has the effect of slowing contraction of the heart muscle and making it beat with less force. The binding of acetylcholine to M 2 receptors serves to slow heart rate till it reaches normal sinus rhythm.
Describe how Atrial Natriuretic Peptide ANP effect blood volume and pressure. Describe the intrinsic regulatory mechanisms of the heart with a detailed description of the. Describe the mechanisms by which epinephrine affects heart rate.
In the heart acetylcholine activation of muscarinic receptors causes channels in the muscle membrane to let potassium pass. The effect of cholinergic agonists on coronary flow rate and oxygen consumption in isolated perfused rat heart Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology Vol. This is achieved by slowing the rate of depolarization as well as by reducing the conduction velocity through the atrioventricular node.
Epinephrine INCREASES heart rate and contractibility by stimulating the sinoatrial SA node and the atrioventricular AV node and enhancing Ca2 ion release via second messenger. The effect of acetylcholine on cardiac muscle however is very different from its effects on skeletal or smooth muscle. Heart Rate drug effects Muscle Contraction.
The vertebrate heart contracts spontaneously but the force and frequency of contration are increased by norepinephrine NE release from sympathetic nerves and acetylcholine ACh released from parasympathetic nerves. The nervous system releases the hormone acetylcholine to slow the heart rate. The known vagolytic effect of quinidine has been termed atropine-like This effect was studied in vitro and in vivo.
Acetylcholine via activation of cell surface receptors in the sinoatrial node pacemaker called acetylcholine muscarinic receptors. This neurotransmitter is responsible for increasing the blood flow of the gastrointestinal tract increases gastrointestinal muscle tone increases gastrointestinal endocrine secretions and decreases heart rate. Parasympathetic impulses and.
In skeletal muscle acetylcholine neurotransmission has an excitatory effect at neuromuscular junctions. Describe the mechanisms by which epinephrine affects heart rate. In this episode Leslie discusses the effect of adrenaline and acetylcholine on heart rate.
1 Mechanisms of methacholine-induced coronary vasospasm in an experimental model of variant angina in the anesthetized rat. This occurs after feeding during sleep and during breath-holding and swimming. In the heart acetylcholine activation of muscarinic receptors causes channels in the muscle membrane to let potassium pass.
In the awake dog ACh caused a triphasic change in HRa rise fall and secondary rise. The stimulating effect of acetylcholine can also be demon-strated in experiments on the frogs heart. If a drop of acetylcholine 1.
The effect of acetylcholine chloride ACh on heart rate HR and blood pressure BP was studied in four dogs awake and under anesthesia by means of pentobarbital sodium. Describe the mechanisms by which atropine followed by acetylcholine affects heart rate. Unlike atropine quinidine was not found to exert any competitive antagonism to acetylcholine at the muscarine-sensitive cholinoceptors of isolated guinea-pig atria.
The three agonists produced increases in contractile force heart rate and ventricular glycogen phosphorylase activity. Furthermore acetylcholine can initiate and maintain slow modulation mechanisms with soluble intracellular messengers kinase activation and phosphorylation. Acetylcholine DECREASES heart rate by hyperpolarizing pacemaker cells in the cardiac muscle by opening potassium ion channels.
Functional Effects Of Acetylcholine Ach And Isoprenaline Iso Download Scientific Diagram

Acetylcholine How And Why To Optimize The Synthesis Of This Vital Neurotransmitter
0 Comments